What is the difference between Forced Download and Redirect Download?
Easy Digital Downloads can be configured to deliver files to customers in two ways, ‘Redirect’ and ‘Forced’. While ultimately both of these methods result in the same goal of the customer downloading a file, there are unique cases in which you’d want to use one or the other.
This setting is located in Downloads > Settings > Misc > File Download.
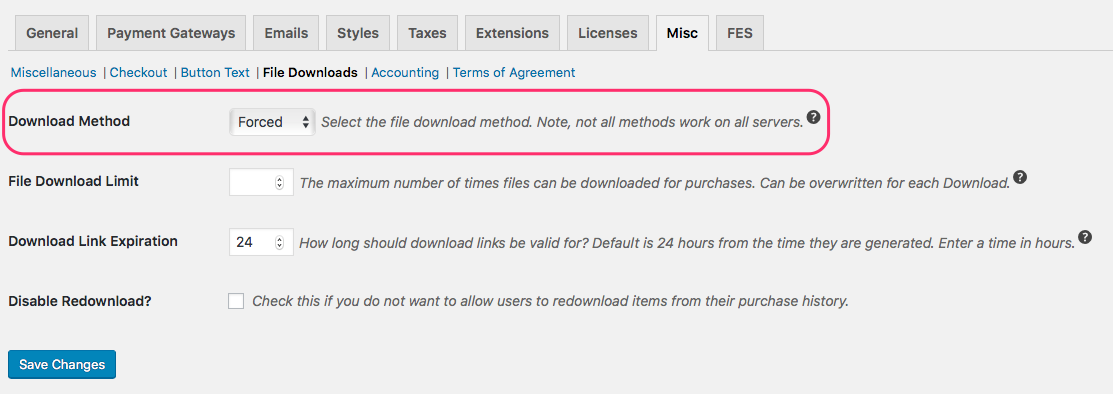
Forced
With the forced method, Easy Digital Downloads breaks the file into smaller pieces and delivers them to the browser without redirecting the user to the actual file. This is beneficial for advanced hosting configurations where files may not be stored in the default directories, or delivered via a content delivery network (CDN).
Due to its consistency in multiple platforms and better file protection, ‘forced’ is the default method.
Because Easy Digital Downloads uses PHP to process the file with the ‘forced’ method, larger files can cause problems with delivery, resulting in hitting the ‘max execution time’ of the server. If user’s are getting 404 or 403 errors when trying to access their purchased files when using the ‘forced’ method, changing to the ‘redirect’ method can help resolve this.
Redirect
The Redirect method is the most straight forward of the two, and works by telling the user’s browser the location of the file, and it then starts the process of downloading it directly from the server. This method of delivering files is best suited for use when certain server configurations do not support the Forced (default) file delivery method, or files are being hosted by a 3rd party (Amazon S3 or Dropbox) that does not support the Forced method. If you do need to use the ‘Redirect’ method for self hosted files (files in the /edd/ directory), it’s advisable to use the ‘Symlink’ option if possible.
The redirect method without symlink, while self hosting files, could result in customers who are downloading files to see the direct path to the file, so the above recommendations should be used.
This does rely on the browser to handle the bulk of the work, and depending on browser configuration can result in unexpected results for some filetypes.
It’s best to use the ‘redirect’ method for large files. Also, we recommended hosting large files on Amazon S3 or Dropbox.
Note: The symlink setting does not apply to Amazon S3 or Dropbox.